Velocity Of Geostationary Satellite To Earth Is

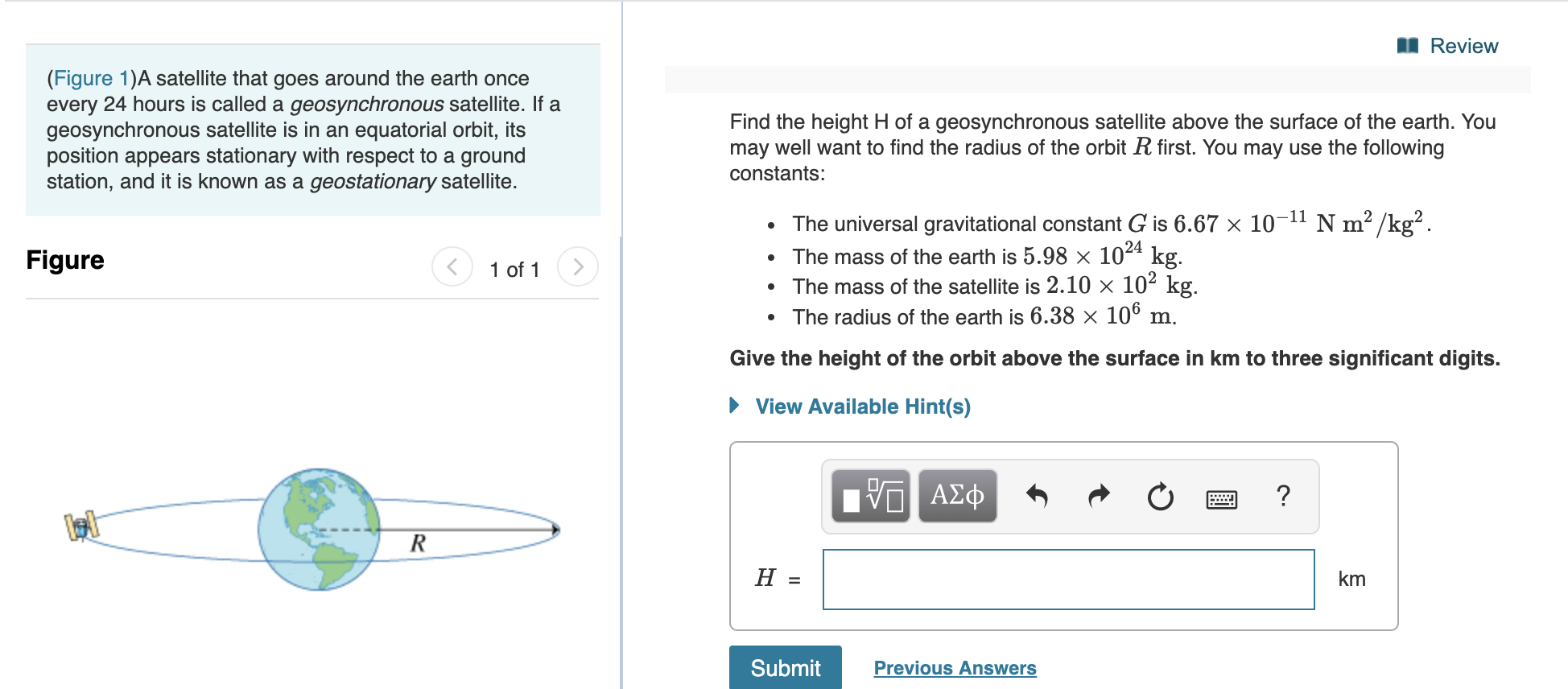
A satellite can be in a geostationary orbit around earth at a distance r from the centre.
Velocity of geostationary satellite to earth is. To be geostationary a satellite needs to revolute at the velocity of about 11060 km h or 3075 m s. Because the satellite stays right over the same spot all the time this kind of orbit is called geostationary geostationary orbits are ideal for weather satellites and communications satellites. Such orbit is called geostationary orbit. The period of the satellite is one day or approximately 24 hours.
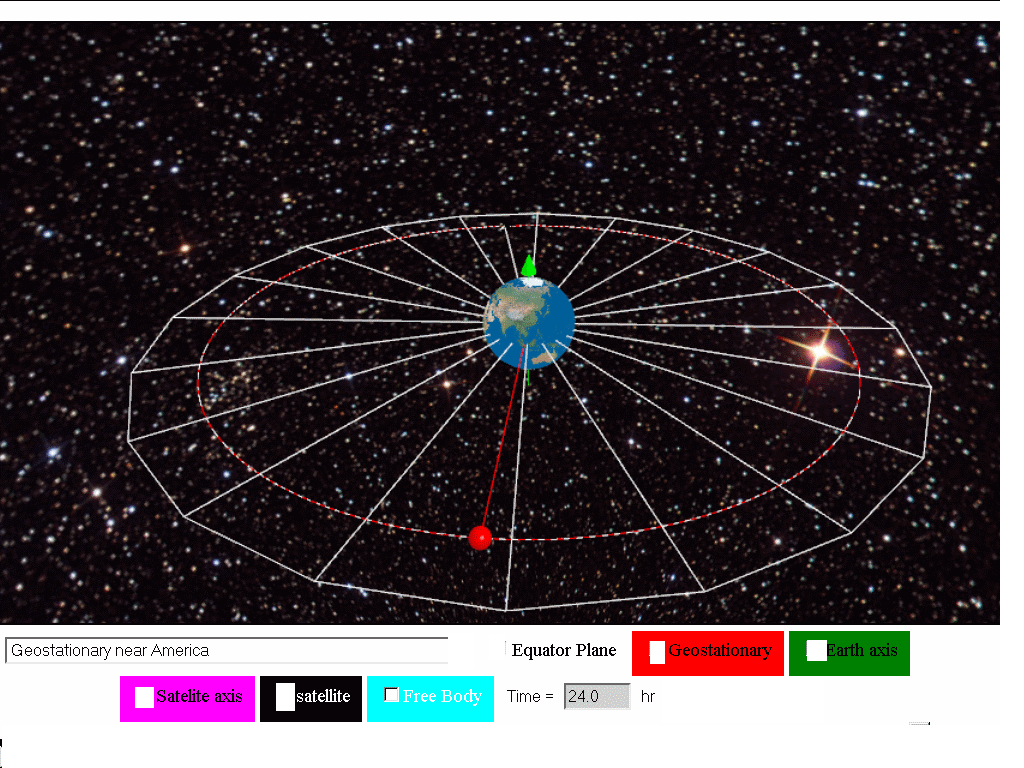
The time period for the geostationary satellite is same as that for the earth i e 24 hours. Since earth also rotates once in 24 hours a satellite at 22 223 miles altitude stays in a fixed position relative to a point on earth s surface. The name geostationary satellite comes from the fact that it apparently appears stationary from the earth. A geostationary orbit also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit geo is a circular geosynchronous orbit 35 786 kilometres 22 236 miles above earth s equator and following the direction of earth s rotation.
At this velocity it is synchronous with the earth and becomes geostationary. 29 814 47129 29 814 4712º 0 0î km ů 2 1748 2 174ỹ 0 02 km s the moon which has a mass of 7 347x1022 kg has the following radius and velocity vectors relative to the center of the earth. In space gravity supplies the centripetal force that causes satellites like the moon to orbit larger bodies like the earth. By steven holzner.
ř 363 625 0 oý 0 0î km û 0 0 0 944679. A geostationary orbit is a circular orbit directly above the earth s equator approximately 35 786 km above ground. Any point on the equator plane revolves about the earth in the same direction and with the same period as the earth s rotation. The angular velocity of any revolving body is th.
If the angular velocity of earth about its axis doubles a satellite can now be in a geostationary orbit around the earth if its distance from the centre is.