Variable Beam Expander Theory

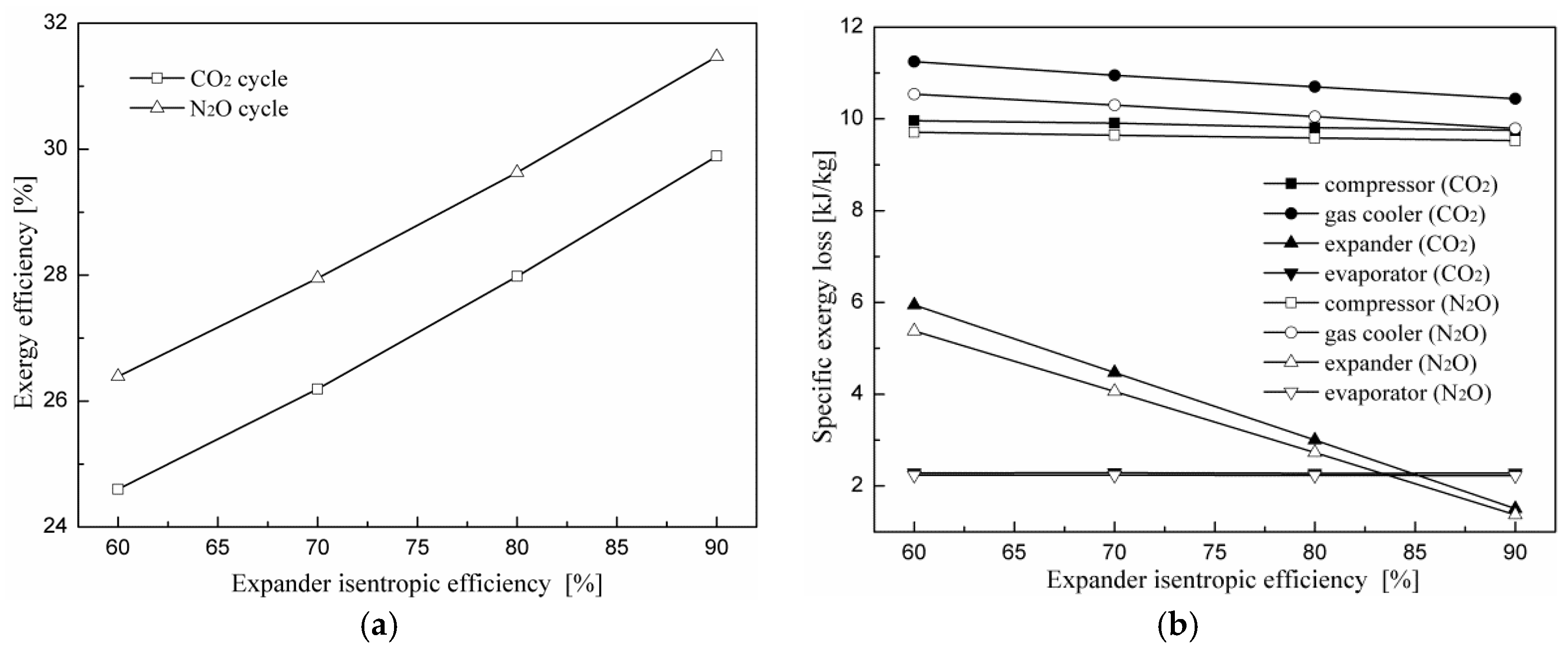
Our variable beam expanders allow separate magnification and divergence adjustment.
Variable beam expander theory. From 2 to 5 or from 5 to 10. 1 magnification power f 1 f 2 magnification power f 1 f 2. By expanding a beam prior to focusing smaller focal spot sizes can be achieved. The beam expander contains a fixed lens at the front followed by two movable lenses.
Thorlabs 0 5x to 2x galilean variable beam expanders reducers allow the user to easily adjust the beam diameter without altering the alignment of the optical setup. Beam expanders thorlabs galilean type beam expanders which are available in both fixed and variable magnification options are offered for use in the uv visible near infrared and mid infrared spectral ranges. There are variable beam expanders zoom expanders i e devices where the magnification can be adjusted in a certain range e g. A beam expander with adjustable magnification.
The magnification of a galilean beam expander is determined by the following equations. Where f 1 is the focal length of the positive lens and f 2 is the focal length of the negative lens. Techspec research grade variable beam expanders rvbx are ideal for high power laser applications where magnification changes may be required such as prototyping or r d. Various magnifications are available but it is important to ensure that the input and output beams clear the apertures.
The mechanics used to focus a beam expander or change the magnification of a variable beam expander are typically classified into two different types. A beam expander is a two or more element optical system that changes the beam s size and divergence characteristics. The fixed magnification sliding lens beam expanders are offered with optics that have either narrowband or wideband ar coatings. These variable magnification zoom beam expanders are designed for required wavelength and each type of our beam expanders has a divergence adjustability.
The design is compact and suitable for an industrial environment. The zoom is adjusted by turning the magnification. 2 optical track length f 1 f 2 optical track length f 1 f 2. Once the desired beam size and divergence is reached the position can be locked with two sets of screws.
Those contain at least three lenses and some fine mechanics to adjust the position of at least one of them. Beam expanders improve a beam s collimation. Rotating focusing mechanisms such as threaded focusing tubes rotate the optical elements during translation. All optical elements of beam expanders are made of fused silica with high lidt coatings and provide stable and reliable performance even using them with high power lasers.