Uses Of Diamond And Graphite In Chemistry

Graphite is insoluble in water and organic solvents for the same reason that diamond is insoluble.
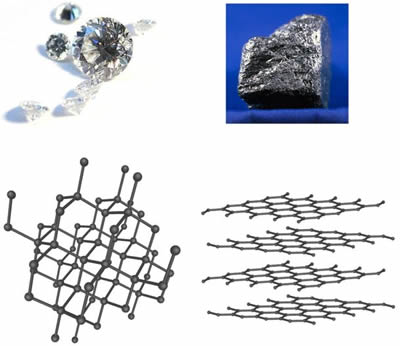
Uses of diamond and graphite in chemistry. Both are made of carbon atoms entirely. This is because of the relatively large amount of space that is wasted between the sheets. This lesson describes the relationship between the structure and function of the giant covalent substances graphite and diamond. These minerals in general are known to be as polymorphs having the same type of chemistry but of the various crystalline structures.
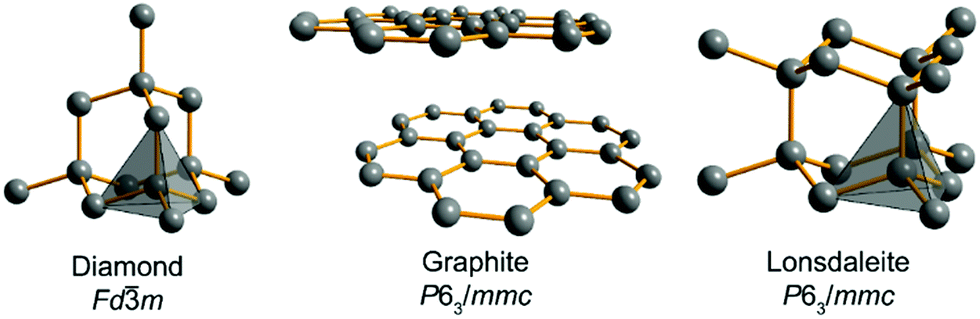
Diamonds so prepared are called synthetic or artificial diamonds. Diamond has a tetrahedral structure where as graphite has an hexagonal arrangement. Diamond and graphite both are known as the allotropes of carbon. Diamonds usually have eight sides forming double pyramids.
When you use a pencil sheets are rubbed off and stick to the paper. The dispersion of graphite in oil is known as oil dag and in water is known as aqua dag. Graphene a naturally occurring ingredient in graphite has unique physical properties and is one of the strongest known substances. Makes diamond useful for cutting tools such as diamond tipped glass cutters and oil rig drills.
Carbon atoms in diamond form a tetrahedral arrangement properties and uses. These minerals chemically consist of carbon atoms with different physical properties. Synthetic diamonds are widely used in industry in cutting and grinding tools. Attractions between solvent molecules.
Mixed with clay it is used in lead pencils. Graphite is used as lubricant either as a powder or as a dispersion in oil or water. The powerpoint and accompanying resource have been designed to cover points 1 35 1 36 and 1 37 of the edexcel gcse chemistry specification also covers those same points in the chemistry section of the combined science course. Graphite is mostly used for refractory battery steel expanded graphite brake linings foundry facings and lubricants.
Diamond and graphite are allot ropes of each other. Graphite is a stable form of naturally occurring carbon also known as plumbago blacklead or mineral carbon. Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which. Solid carbon comes in different forms known as allotropes depending on the type of chemical bond.
Diamond is a solid form of pure carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal. The low density 2 26 g cm 3 of graphite is due to large distance between different layers of carbon atoms. The rigid network of carbon atoms held together by strong covalent bonds makes diamond very hard. The chemical properties of synthetic and natural diamonds are the same.